This topic describes how to access a Network File System (NFS) share of a file gateway from a Linux Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
Prerequisites
An NFS share is created. For more information, see Create a share.
Install an NFS client
Before you mount an NFS share, you must install an NFS client on the machine.
Log on to the machine.
Run the following command to install the NFS client:
The following commands install an NFS client on Ubuntu and CentOS. For more information about how to install an NFS client on other distributions, see the official NFS documentation.
Ubuntu:
apt-get install nfs-commonCentOS:
yum install -y nfs-utils
Manually mount an NFS share
Log on to the ECS console.
Connect to your Linux ECS instance. For more information, see Connect to an instance.
On the ECS instance, run the following command to mount an NFS share to a local directory of the client:
IPv4:
mount.nfs 192.168.0.0:/shares local-directoryIPv6:
mount.nfs [2408:4004:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff]:/shares local-directoryNFS version 3:
Run the following command to query the mount target. In this example, the mount target is
192.168.0.0:/shares.showmount -e <gateway IP address>Run the following command to mount the share:
mount -t nfs -o vers=3,proto=tcp,nolock 192.168.0.0:/shares local-directory
NoteYou can mount a share over IPv6 only in the China (Hohhot) region. Make sure that the virtual private cloud (VPC) and vSwitch of the gateway support IPv6.
If you want to mount a share over IPv6, make sure that an IPv6 address is configured for the client on the ECS instance.
If the VPC and vSwitch of an existing gateway support IPv6, you can obtain an IPv6 mount target after you enable IPv6 support for the gateway. By default, new gateways created in this IPv6-compatible VPC support IPv6.
Command description:
192.168.0.0:/sharesis the mount target, which consists of the IPv4 address of the gateway and the share name. Replace them with your actual information. You can check the mount target on the Shares tab of the gateway details page in the Cloud Storage Gateway (CSG) console.[2408:4004:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff]:/sharesis the mount target, which consists of the IPv6 address of the gateway and the share name. Replace them with your actual information. You can check the mount target on the Shares tab of the gateway details page in the CSG console.local-directoryis the local directory of the client. You must specify a directory that allows read and write operations. You cannot specify a directory that does not exist.noacspecifies that the client obtains the file system metadata from the gateway in real time. You can specify the noac parameter in the mount command if the express synchronization feature is enabled and the share that you want to mount is added to an express synchronization group. This allows you to check the synchronization result on the client at the earliest opportunity. This parameter has an observable impact on the read/write performance of the client. If the client needs to monitor data changes, we recommend that you specify this parameter. If the client requires high write/read performance, we recommend that you do not specify this parameter. The following sample code provides an example of a mount command that includes the noac parameter:mount -t nfs -o nolock,noresvport,noac,lookupcache=none 192.168.0.0/shares local-directory
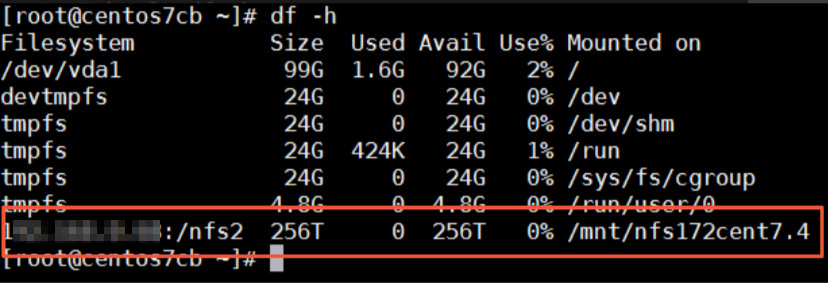
Run the df -h command to view the mount result.
If the output is similar to the following information, the NFS share is mounted.
 Note
NoteAfter the NFS share is mounted, you can view the capacity of the file system that is managed by the NFS share. Object Storage Service (OSS) provides unlimited storage capacity. For the file system capacity supported for individual gateway specifications, see Specifications.
Access an NFS share
After an NFS share is mounted, you can access the NFS share in the same way that you access a local directory. If you have write permissions on the share, you can write data to the share. If you have read-only permissions on the share, you can only read data from the share.
A share of a gateway is synchronized with the OSS bucket associated with the share. When you perform operations on a share, the changes in the share are also applied to the associated OSS bucket.
Unmount a share
To unmount a share, run the umount local-directory command, where local-directory is the local directory on which the share is mounted.
Automatically mount an NFS share
If you manually mount an NFS share to a Linux client, the NFS share mount does not persist after a client restart. You can configure the Linux client to automatically mount an NFS share upon ECS instance restart by using the /etc/fstab (recommended) or /etc/rc.local file.
Before you configure a share to be automatically mounted, make sure that you have manually mounted the share. This prevents automatic mount failures after an ECS instance restart.
Open the configuration file and add the mount configurations.
Method 1 (recommend): Open the /etc/fstab configuration file and add the mount configurations.
NoteIf your client runs CentOS 6, perform the following steps first:
Run the
chkconfig netfs oncommand to enable NetFS startup upon system boot.Open the /etc/netconfig file and comment out inet6-related information.
To mount the NFS share by using NFS version 4, add the following mount configurations:
IPv4:
192.168.0.0:/shares local-directory nfs defaults 0 0IPv6:
[2408:4004:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff]:/shares local-directory nfs defaults 0 0
To mount the NFS share by using NFS version 3, add the following mount configurations:
IPv4:
192.168.0.0:/shares local-directory nfs vers=3.0 defaults 0 0IPv6:
[2408:4004:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff]:/shares local-directory nfs vers=3.0 defaults 0 0
Method 2: Open the /etc/rc.local configuration file and add the mount configurations.
NoteBefore you edit the /etc/rc.local file, make sure that you have the execute permission on the /etc/rc.local and /etc/rc.d/rc.local. For example, in CentOS 7.x, the execute permission is not granted by default. You must have the execute permission to edit the /etc/rc.local file.
To mount the NFS share by using NFS version 4, add the following mount configurations:
IPv4:
sudo mount.nfs 192.168.0.0:/shares local-directoryIPv6:
sudo mount.nfs [2408:4004:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff]:/shares local-directory
To mount the NFS share by using NFS version 3, add the following mount configurations:
IPv4:
sudo mount -t nfs -o vers=3,proto=tcp,nolock 192.168.0.0:/shares local-directoryIPv6:
sudo mount -t nfs -o vers=3,proto=tcp,nolock [2408:4004:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff]:/shares local-directory
Command description:
192.168.0.0:/sharesis the mount target, which consists of the IPv4 address of the gateway and the share name. Replace them with your actual information. You can check the mount target on the Shares tab of the gateway details page in the Cloud Storage Gateway (CSG) console.[2408:4004:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff]:/sharesis the mount target, which consists of the IPv6 address of the gateway and the share name. Replace them with your actual information. You can check the mount target on the Shares tab of the gateway details page in the CSG console.local-directoryis the local directory of the client. You must specify a directory that allows read and write operations. You cannot specify a directory that does not exist.noacspecifies that the client obtains the file system metadata from the gateway in real time. You can specify the noac parameter in the mount command if the express synchronization feature is enabled and the share that you want to mount is added to an express synchronization group. This allows you to check the synchronization result on the client at the earliest opportunity. This parameter has an observable impact on the read/write performance of the client. If the client needs to monitor data changes, we recommend that you specify this parameter. If the client requires high write/read performance, we recommend that you do not specify this parameter. The following sample code provides an example of a mount command that includes the noac parameter:mount -t nfs -o nolock,noresvport,noac,lookupcache=none 192.168.0.0/shares local-directory
Run the reboot command to restart the ECS instance.