By Liu Bin (Lingsu)

Circular dependency exceptions at startup often occur.
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'taskPunchEvent': Injection of resource dependencies failed; nested exception is org.
springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'playContentService': Bean with name 'playContentService' has been injected into other be
ans [toVoConvertor] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the bean. Thi
s is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using 'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.
at org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:325)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.populateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1404)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:592)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:515)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.lambda$doGetBean$0(AbstractBeanFactory.java:320)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:222)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:318)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:199)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DependencyDescriptor.resolveCandidate(DependencyDescriptor.java:277)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.doResolveDependency(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1255)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.resolveDependency(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1175)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredFieldElement.inject(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:595)
... 40 more
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'playContentService': Bean with name 'playContentService' has been injecte
d into other beans [toVoConvertor] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version o
f the bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using 'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:622)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:515)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.lambda$doGetBean$0(AbstractBeanFactory.java:320)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:222)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:318)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:204)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.resolveBeanByName(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:452)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.autowireResource(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:527)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.getResource(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:497)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$ResourceElement.getResourceToInject(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:637)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata$InjectedElement.inject(InjectionMetadata.java:180)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata.inject(InjectionMetadata.java:90)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:322)
... 51 moreFocus on the phenomenon instead of other non-standard problems.
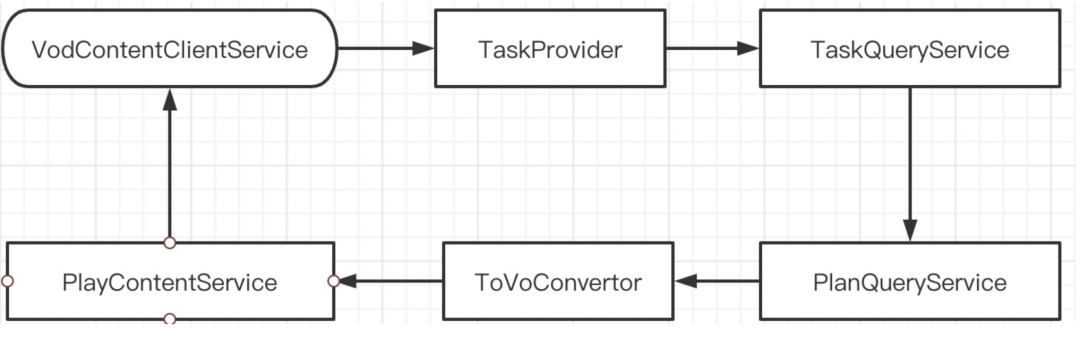
Note: The Spring startup process and the Bean creation initialization process will not be described here.
Spring Bean: Spring-managed instances that have been initialized and can be used later.
-Then, create an instance of the Spring bean based on BeanDefinition.
Java Bean: An object created by a simple constructor in Java.
The user does not manually go to getBean to load and initialize it. It loads when the framework starts.
Spring Create Bean-#DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
//......
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
//FactoryBean interface process
......
}
else {
// The loading entry for a normal bean
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
//......
}Circular Dependencies within the Constructor
// Example of the circular dependency of the constructor.
public class StudentA {
private StudentB studentB ;
public StudentA(StudentB studentB) {
this.studentB = studentB;
}
}
public class StudentB {
private StudentA studentA ;
public StudentB(StudentA studentA) {
this.studentA = studentA;
}
}@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// Property injection
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);Level-2 cache (uninitialized beans exposed in advance with unpopulated properties)
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<>(16);When an AOP scenario exists:
Level-3 cache (bean factory cache that provides proxy opportunities at bean creation)
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16);Circular dependencies are generated when bean is created.
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// Create Bean
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
.....
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Fill in the bean dependency and initialize the bean.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// Fill in the dependent bean instance.
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// Initialize --- Note that BeanPostProcessor may be called in this method.
// A proxy object may be returned when the proxy is applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization, and a different proxy object will be generated if the proxy path is different from the way the proxy was created.
// This results in object inconsistency in circular dependencies.
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
// If there is a circular dependency, ensure that the bean created at the beginning needs to be the bean generated by the circular dependency getEarlyBeanReference.
// getEarlyBeanReference may return a proxy class since the singleton must be globally unique.
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
// The getEarlyBeanReference call is triggered to generate EarlyBean only when circular dependencies exist.
// If no circular dependency exists, getEarlyBeanReference is not triggered. The earlySingletonReference is null and the objectObject is returned.
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
......
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
return exposedObject;
}Level-3 Cache Obtaining Beans
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Obtain beans from level-1 cache (singleton pool).
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Obtain beans from the level-2 cache (incomplete exposure in advance).
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
// The creation factory of level-3 cache bean obtains the bean (can be proxied in advance).
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor Focus -> Father of APC
// Provide the factory singletonFactory.getObject() that creates and returns the proxy in advance. It executes a callback.
//addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) {
Object exposedObject = bean;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// getEarlyBeanReference is the SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor interface definition method.
// This method is critical (constructor inference is also defined here).
if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
exposedObject = ibp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);
}
}
}
return exposedObject;
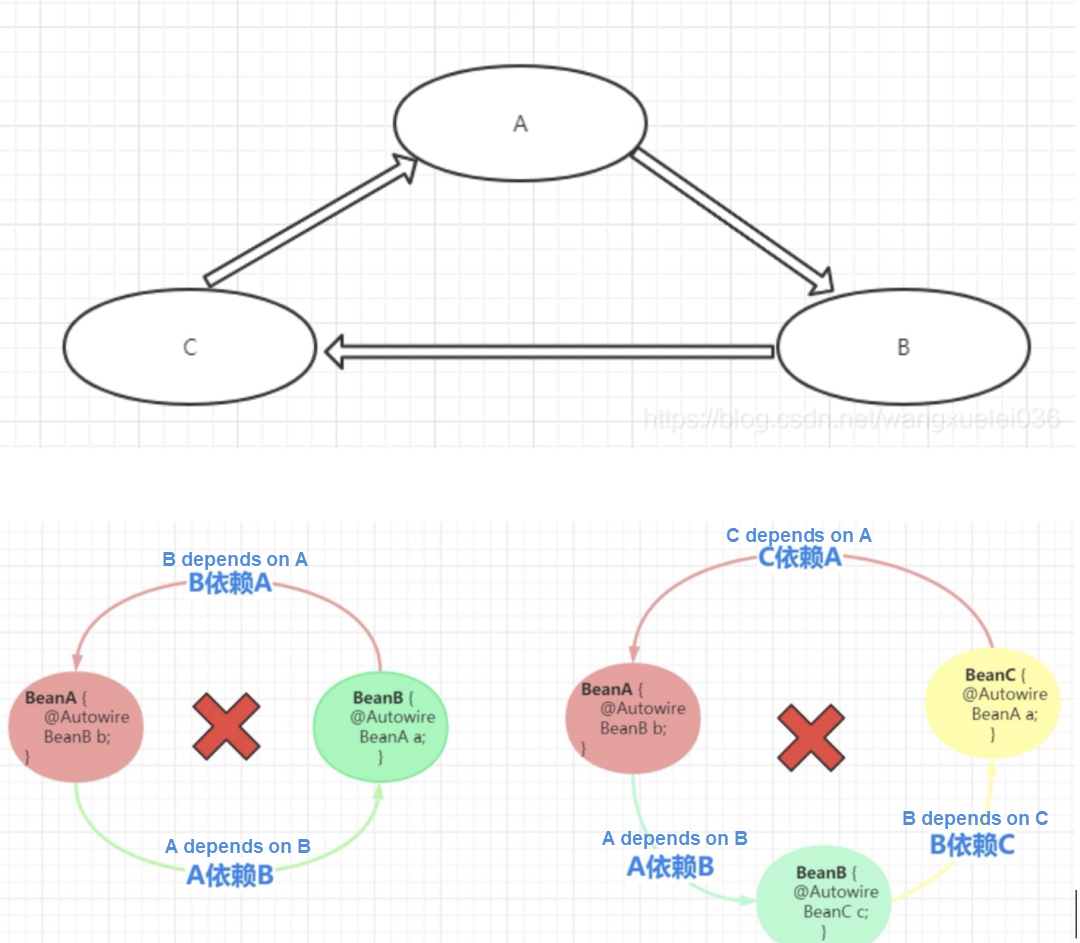
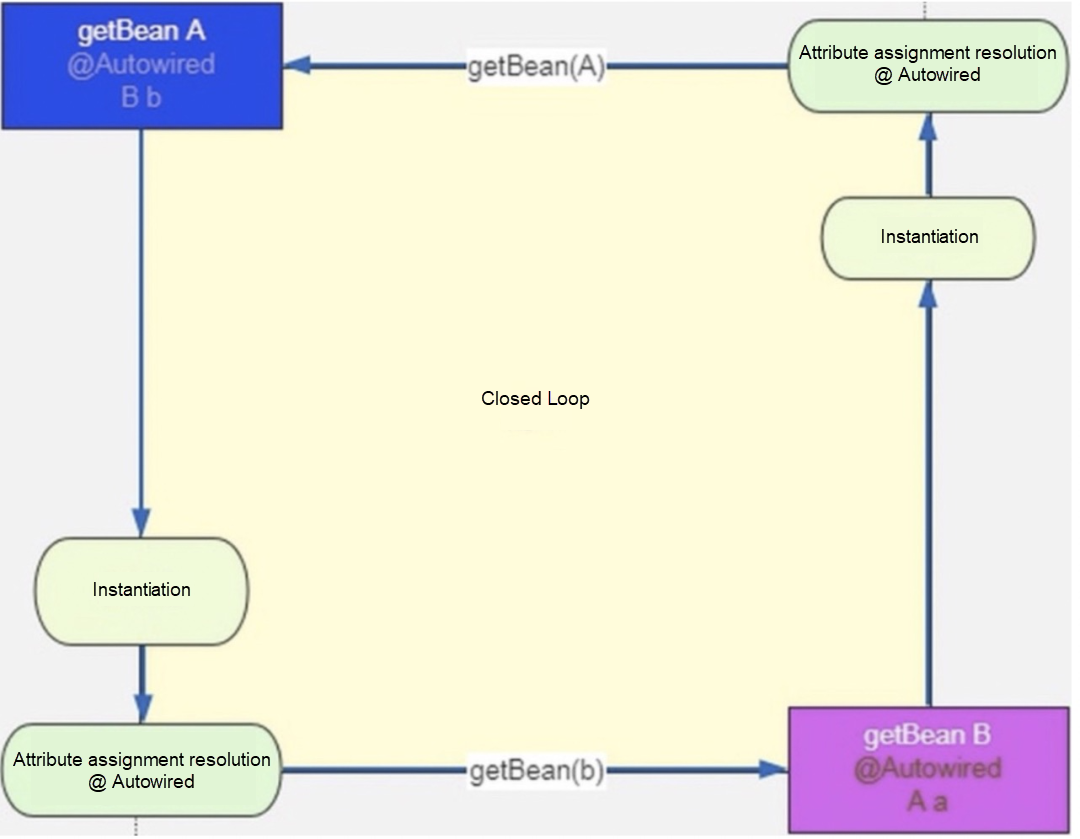
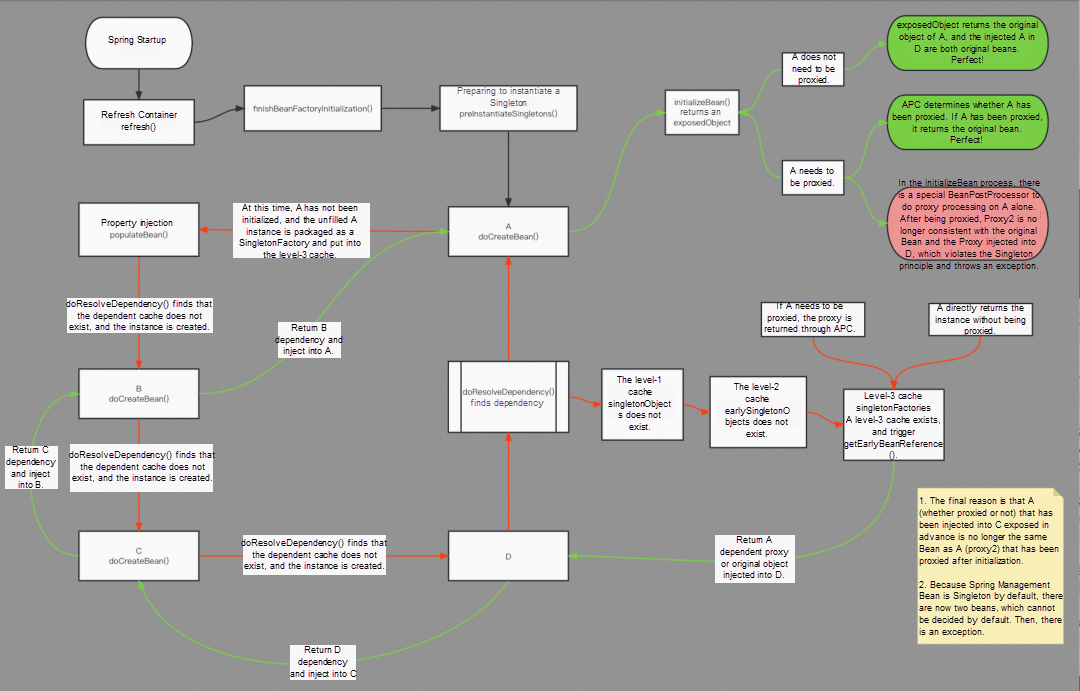
}Popular explanation (omitting many details): A -> B -> C -> A
1. Spring starts to create A: When populateBean() is filled with attributes in A in doCreateBean(), the dependent B object needs to be found. At this time, A has not been initialized, and the original A object is packed into SingletonFactory and put into the Level-3 cache.
2. A depends on B: Therefore, the dependent C object needs to be found when doCreateBean() creates B and fills in the attributes populateBean() of B.
3. C depends on A: Therefore, the dependent A object needs to be found when doCreateBean() creates C and fills in the attributes populateBean() of C.
3.1. At this time, go to the level-1 cache to obtain A because the front edge of A has not been filled and initialized, so it does not exist in the level-1 cache.
3.2. Go to the level-2 cache to obtain A because the front of A has not been filled and initialized, so it does not exist in the level-2 cache.
3.3. Go to the level-3 cache to get A. In the first step, A is packaged as SingletonFactory and put into the level-3 cache, so the object of A can be obtained from the level-3 cache.
3.3.1. A obtained at this time will perform a dynamic proxy on A if necessary and return the proxy object.
3.3.2. Otherwise, the unfilled, uninitialized original object A is returned if no proxy is needed.
3.4. Get the object A and inject it into C. Initialize C and return the C object.
4. The C object is returned and injected into B. Then, B is initialized, and the B object is returned.
5. The B object is returned and injected into A, and then A is initialized. There is a problem:
5.1. If the next initialization A does not need to be proxied.
5.1.1. ExposedObject returns the original object of A. In this case, the original bean is injected into A in C. Perfect.
5.2. If the next initialization A does not need to be proxied.
5.2.1. APC checks whether A has been proxied when it was created before, according to the cache. If it has been proxied, it directly returns the original object, which is consistent with A's original. Perfect.
5.2.2. However, if there are other unique BeanPostProcessor in the initialization process of A and the proxy mode of A is handled separately, the proxy2 (after being proxied) is no longer consistent with the original Bean, and the Proxy of A injected into C. An exception is thrown.
6. Summary
6.1. The ultimate reason is that A (whether proxied or not) that has been injected into C exposed in advance is no longer the same Bean as A (proxy2) that has been proxied after initialization.
6.2. Since Spring-managed Bean is Singleton by default, there are two beans that cannot be decided by default. An exception is thrown.
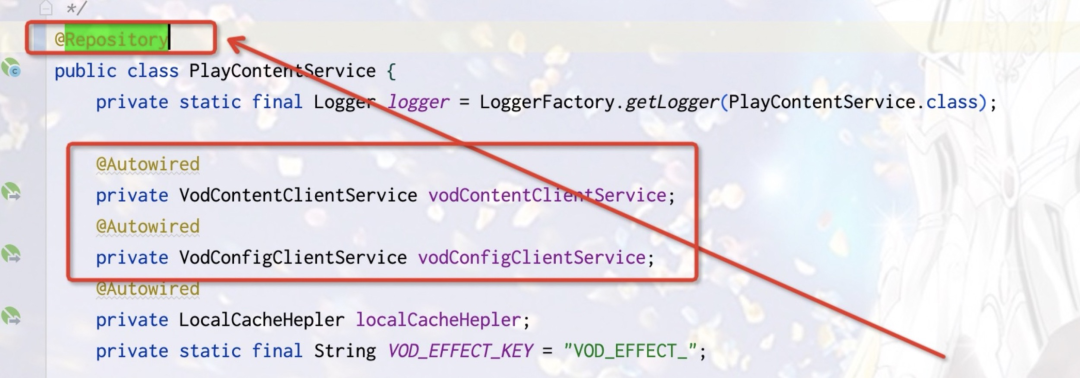
@Respository
@Asyn
By default, Spring guarantees that there can only be one APC of AOP in a container. If it is manually added or customized, multiple APCs will occur.
If there are three, they will be overwritten according to the priority. Otherwise, one will be registered. There will only always be one APCAopConfigUtils.
static {
APC_PRIORITY_LIST.add(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class);
APC_PRIORITY_LIST.add(AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class);
APC_PRIORITY_LIST.add(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
}
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(
Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {
// Because the three APCs have a parent-child relationship, the priority is automatically adjusted according to the specified registered APC, thus ensuring that only one APC exists.
// If APC is not specified, the default value is InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
}
}
return null;
}
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}When there are multiple APCs (such as circular dependencies), put level-3 cache logic before triggering…
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));Thereby triggering getEarlyBeanReference of multiple APCs:
protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) {
Object exposedObject = bean;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
// At this time, if there are multiple APCs, the getEarlyBeanReference is executed in sequence to return multiple layers of proxy objects.
for (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().smartInstantiationAware) {
exposedObject = bp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);
}
}
return exposedObject;
}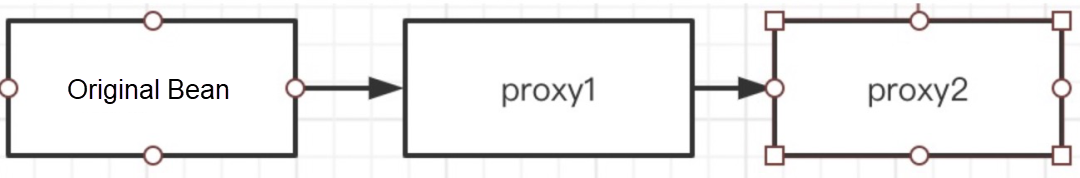
Finally, proxy2 will be injected into the dependent Bean. For example, A-proxy2 injected into B has multiple multi-layer proxies. There are no problems with getEarlyBeanReference, but when it executes to initialization:
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
// Note that this Bean is the original object. Each APC caches its proxy class, but when there are multiple APCs, the subsequent APC cache is indeed the proxy of the proxy class.
// If the second APC is BeanNameAutoProxyCreator, its cache is class of proxy1. The original class has not been proxied in this APC.
// Therefore, the original class will be proxied twice at this time, resulting in Proxy3.
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
// Return to the node that this loop depends on initially instantiated: A->B->C->A. This is the creation process of A.
// At this time, A generates A->proxy2 by getEarlyBeanReference and injects it into C.
// The direct instance creation of C will not trigger getEarlyBeanReference and is injected into B.
// The direct instance creation of B will not trigger getEarlyBeanReference and is injected into A.
// After the dependency A is processed, continue initializing the initializeBean process-> postProcessAfterInitialization and return proxy3.
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
// The proxy class obtained at this time is proxy2, that is the proxy that has been injected into the dependency class C, so it is not null.
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
// If multiple APCs are used, the initializeBean -> postProcessAfterInitialization function of the previous initializeObject returns proxy3.
// proxy3 != bean is inconsistent and violates the singletion principle. Therefore, a circular dependency exception is thrown.
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
......
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
@Override
public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
this.earlyProxyReferences.put(cacheKey, bean);
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
// After the proxy created by singletonFactory.getObject() is cached in advance, if it is judged again that a proxy is needed here,
// If there is a proxy in the cache, the original bean is directly returned without the need to proxy again, and the earlySingletonReference is directly obtained later.
// Therefore, the objects proxied before and after are consistent.
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory#resolveDependency
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer());
if (Optional.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return createOptionalDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
......
else {
// Process @lazy
Object result = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(
descriptor, requestingBeanName);
if (result == null) {
result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
return result;
}
}
ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver#getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary
public Object getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName) {
return (isLazy(descriptor) ? buildLazyResolutionProxy(descriptor, beanName) : null);
}
ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver#isLazy
// Indicates whether the value is @lazy. If it is, the dependency proxy is created.
protected boolean isLazy(DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
for (Annotation ann : descriptor.getAnnotations()) {
Lazy lazy = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(ann, Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null && lazy.value()) {
return true;
}
}
.......
}import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.dao.annotation.PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @author: Superizer
*/
@Component
public class MainSpringCircularDependencyTester
{
@Test
public void springCircularDependencyTest()
{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringCircularDependencyConfig.class);
X x = ac.getBean(X.class);
System.out.println("Spring bean X =" + x.getClass().getName());
x.display();
Y y = ac.getBean(Y.class);
System.out.println("Spring bean Y =" + y.getClass().getName());
y.display();
Z z = ac.getBean(Z.class);
System.out.println("Spring bean Z =" + z.getClass().getName());
z.display();
System.out.println("******************Main********************");
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.myself.demo.spring.v5.circular.dependency")
// @EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ConditionalOnClass(PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor.class)
static class SpringCircularDependencyConfig{
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.dao.exceptiontranslation", name = "enabled",
matchIfMissing = true)
public static PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor
persistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor(Environment environment) {
PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor postProcessor = new PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor();
boolean proxyTargetClass = environment.getProperty(
"spring.aop.proxy-target-class", Boolean.class, Boolean.TRUE);
postProcessor.setProxyTargetClass(proxyTargetClass);
return postProcessor;
}
}
abstract static class A {
public abstract A injectSources();
public abstract A self();
public void display(){
System.out.println("injectSources:" + injectSources().getClass().getName());
System.out.println("*******************************************************");
}
}
// X, Y, Z. As long as the first class X in the circular dependency has the annotation @Repository, the circular dependency exception will occur.
// Execute singletonFactory.getObject() of X to return the original object, but during initialization,
// When the PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor is executed, the proxy class is returned by the separate proxy logic.
//exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
@Repository
// @Component
static class X extends A{
@Resource
private Y y;
@Override
public Y injectSources()
{
return y;
}
@Override
public X self() {
return this;
}
}
@Component
// @Repository
static class Y extends A{
@Resource
private Z z;
@Override
public Z injectSources() {
return z;
}
@Override
public Y self()
{
return this;
}
}
@Component
// @Repository
static class Z extends A{
@Resource
private X x;
@Override
public X injectSources()
{
return x;
}
@Override
public Z self()
{
return this;
}
}
}import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.aop.ClassFilter;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodMatcher;
import org.springframework.aop.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator;
import org.springframework.aop.support.AbstractExpressionPointcut;
import org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author: Superizer
* Copyright (C) 2021
* All rights reserved
*/
@Component
public class MainSpringCircularDependencyV2Tester
{
@Test
public void circularDependencyV2Tester()
{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringCircularDependencyConfig.class);
A a = ac.getBean(A.class);
System.out.println("Spring bean A =" + a.getClass().getName());
a.display();
B y = ac.getBean(B.class);
System.out.println("Spring bean B =" + y.getClass().getName());
y.display();
C z = ac.getBean(C.class);
System.out.println("Spring bean C =" + z.getClass().getName());
z.display();
System.out.println("******************Main********************");
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.myself.demo.spring.v5.circular.dependency.v2")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
static class SpringCircularDependencyConfig {
@Bean
public DefaultPointcutAdvisor defaultPointcutAdvisor() {
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor();
Pointcut pointcut = new AbstractExpressionPointcut() {
@Override
public ClassFilter getClassFilter() {
return (tmp) -> {
String name = tmp.getName();
if(name.equals(A.class.getName())) {
return true;
}
return false;
};
}
@Override
public MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher() {
return MethodMatcher.TRUE;
}
};
advisor.setPointcut(pointcut);
advisor.setAdvice(new SpringAopAroundMethod());
advisor.setOrder(0);
return advisor;
}
@Bean
public BeanNameAutoProxyCreator beanNameAutoProxyCreator() {
BeanNameAutoProxyCreator apc = new BeanNameAutoProxyCreator();
apc.setBeanNames("a");
apc.setOrder(-1);
apc.setProxyTargetClass(true);
return apc;
}
}
abstract static class G {
public abstract G injectSources();
public abstract G self();
public void display(){
System.out.println("injectSources:" + injectSources().getClass().getName());
System.out.println("*******************************************************");
}
}
@Component(value = "a")
static class A extends G {
@Resource
private B b;
@Override
public B injectSources()
{
return b;
}
@Override
public A self() {
return this;
}
}
@Component
static class B extends G {
@Resource
private C c;
@Override
public C injectSources() {
return c;
}
@Override
public B self()
{
return this;
}
}
@Component
static class C extends G {
@Resource
private A a;
@Override
public A injectSources()
{
return a;
}
@Override
public C self()
{
return this;
}
}
static class SpringAopAroundMethod implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Aop Before method!");
try {
Object result = methodInvocation.proceed();
System.out.println("Aop after method!");
return result;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("Aop throw exception!");
throw e;
}
}
}
}Circular dependencies reflect problems in the design of the code structure. Theoretically, circular dependencies should be layered, common parts should be extracted, and each functional class should rely on the common parts again.
However, in complex code, there are too many service and manager classes calling each other, and there will always be circular dependencies between some classes. Sometimes, we find that when using Spring for dependency injection, there are circular dependencies between Beans, but the code has a high probability of normal work, and there seems to be no bug.
Many of you may ask how can this kind of violation of causality happen. Yes, this is not taken for granted. Spring has carried too much for us, but it is not an excuse for laziness. We should standardize the design and code and try our best to avoid this kind of circular dependency.
Is Your Redis Slowing Down? – Part 2: Optimizing and Improving Performance

1,340 posts | 470 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - May 7, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Community - August 17, 2023
Alibaba Developer - August 18, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - August 26, 2021
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - March 20, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - July 26, 2023

1,340 posts | 470 followers
Follow Dedicated DingTalk Solution
Dedicated DingTalk Solution
Organizations of any size can leverage DingTalk’s enterprise-exclusive APIs to quickly create customized mobile workspaces on DingTalk or mobile applications while taking full control of your business data.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Community