This article is a part of the One-stop Big Data Development and Governance DataWorks Use Collection.
By Tang Chen, Product Manager of DataWorks
When we talk about data governance, we often discuss it with the concept of data management together. When developers design data governance functions in DataWorks, they mainly refer to three major theoretical bases in the data management field. The first is the knowledge system of the Data Management Association, which are the well-known DAMA and DMBOK2. The second is the Data Management Capability Maturity Assessment Model (DCMM). The third is the white paper on the management practice of data assets by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT).
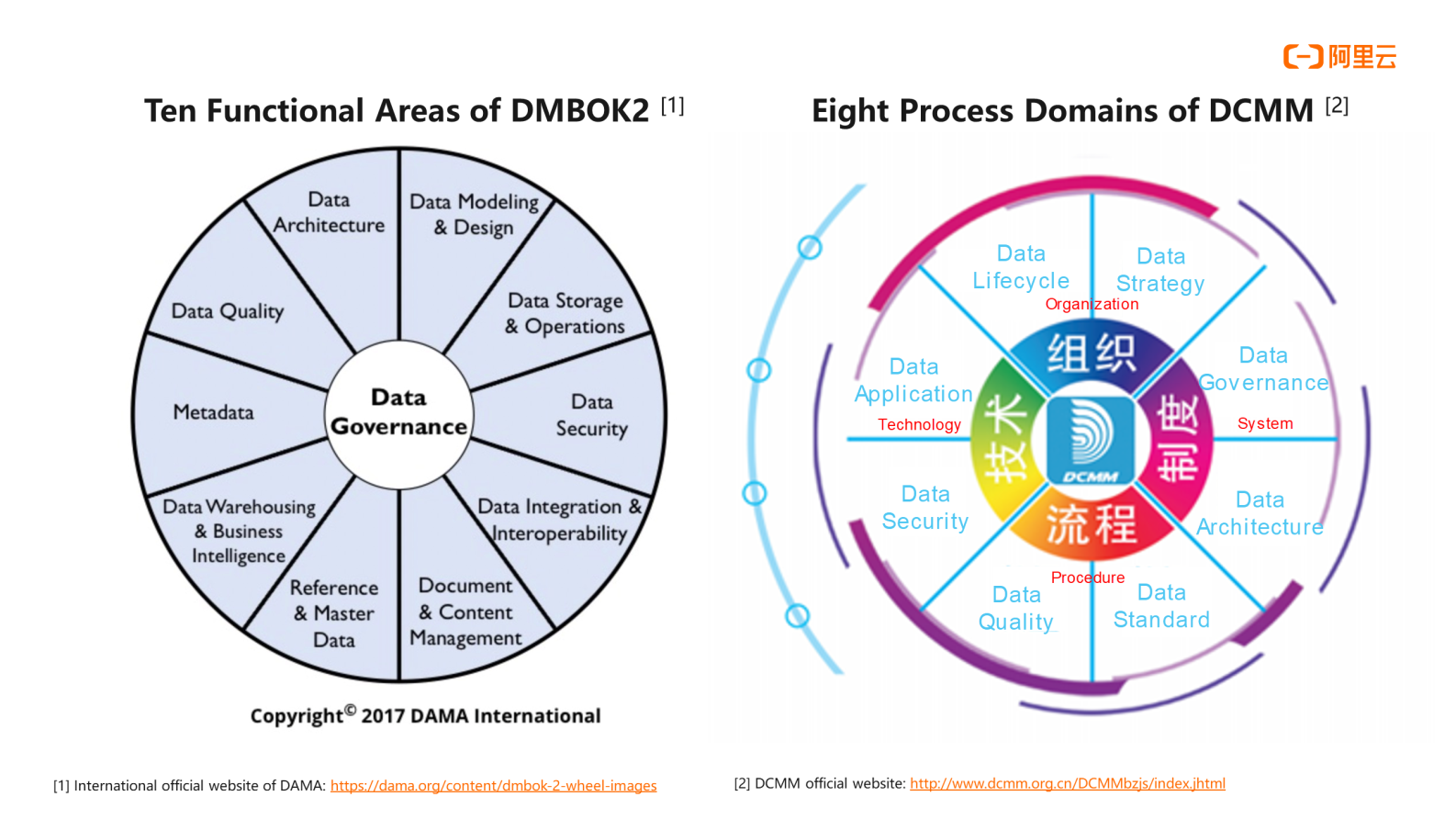
The graphs on the left and right show how DMBOK and DCMM are slightly different in terms of the scope and definition of data management and data governance. DMBOK divides data management into ten functional areas. Data governance is located in the middle and connects the ten functional areas. DCMM defines data management as eight process domains, and data governance is one of the process domains alongside data quality and data security.Differences in the understanding of data management and data governance exist across different organizations and groups in the industry.
DAMS describes data governance as such: During data managing, the process and tools needed for this work belong to the field of data governance to ensure an organization has converted data into useful information. Two concepts are emphasized here. First, data governance is part of data management. Second, the core of data governance is to guarantee processes and supporting tools. DataWorks refers to this definition and designs data governance capabilities, focusing on meeting the requirements of supporting data asset management. Product capacity building is a progressive process, and DataWorks is continuously expanding its functions.
In addition to data governance requirements, we make analyses based on data governance practices in Alibaba and communication with external customers and peers. We find the core requirements of data governance are different according to the different digital transformation stages of enterprises. From an abstract point of view, data governance demand can be divided into five levels. The first level is timeliness, which refers to the timely output of data. The second level is quality, which refers to data quality control and the completeness, correctness, and accuracy of data. The third level is the availability of data. The main emphasis here is on the sharing and use of data, in other words, whether data is easy to find, understand, or reuse. The fourth layer is data security, such as the application and approval of data permissions, process control, identification and protection of sensitive data, and compliance requirements. The fifth layer is cost optimization and control of data production, storage, and use.
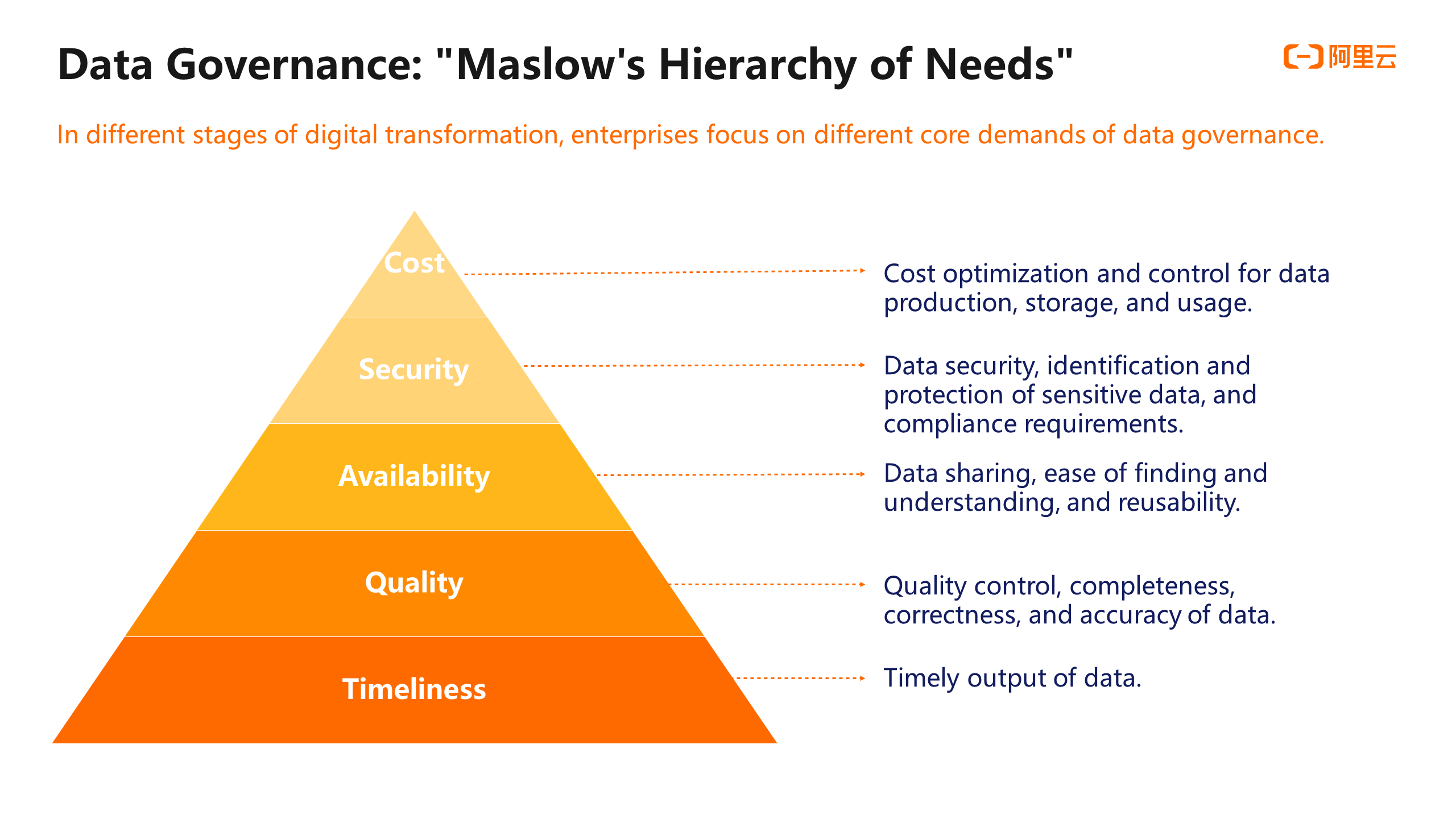
Among these five levels of demand, the lower the demand is on the pyramid, the more basic it is to be met. However, the demands of the upper levels will gradually emerge as the digital transformation process of enterprises deepens. This is also true within Alibaba. Alibaba gave priority to the stable operation of data tasks, the timely output of data, and the data correctness and availability at the initial stage over ten years ago. When these demands are met and guaranteed, the demand at the top of the pyramid, which is cost optimization, becomes the biggest concern of Alibaba currently.
These demands do not have to evolve level by level. At one stage, an enterprise is likely to have multiple levels of demands at the same time, but the focus may be different.
These five levels of demand define a core goal of data governance. The digital transformation of enterprises should treat data as assets to the largest extent to mine value from it. In this process, data governance needs to meet requirements from five aspects: timely output, reliable quality, availability, secure and controllable data, and economic production.
There are two methods in terms of implementation strategies: bottom-up and top-down. The combination of the two methods is proved to be more effective according to practices in Alibaba. The upper level is used to globally plan data, construct organizations, and formulate rules to provide upper-level empowerment for governance. The lower level focuses on sorting out core workflows and building platforms, tools, and operating systems, which can support the implementation of data governance.
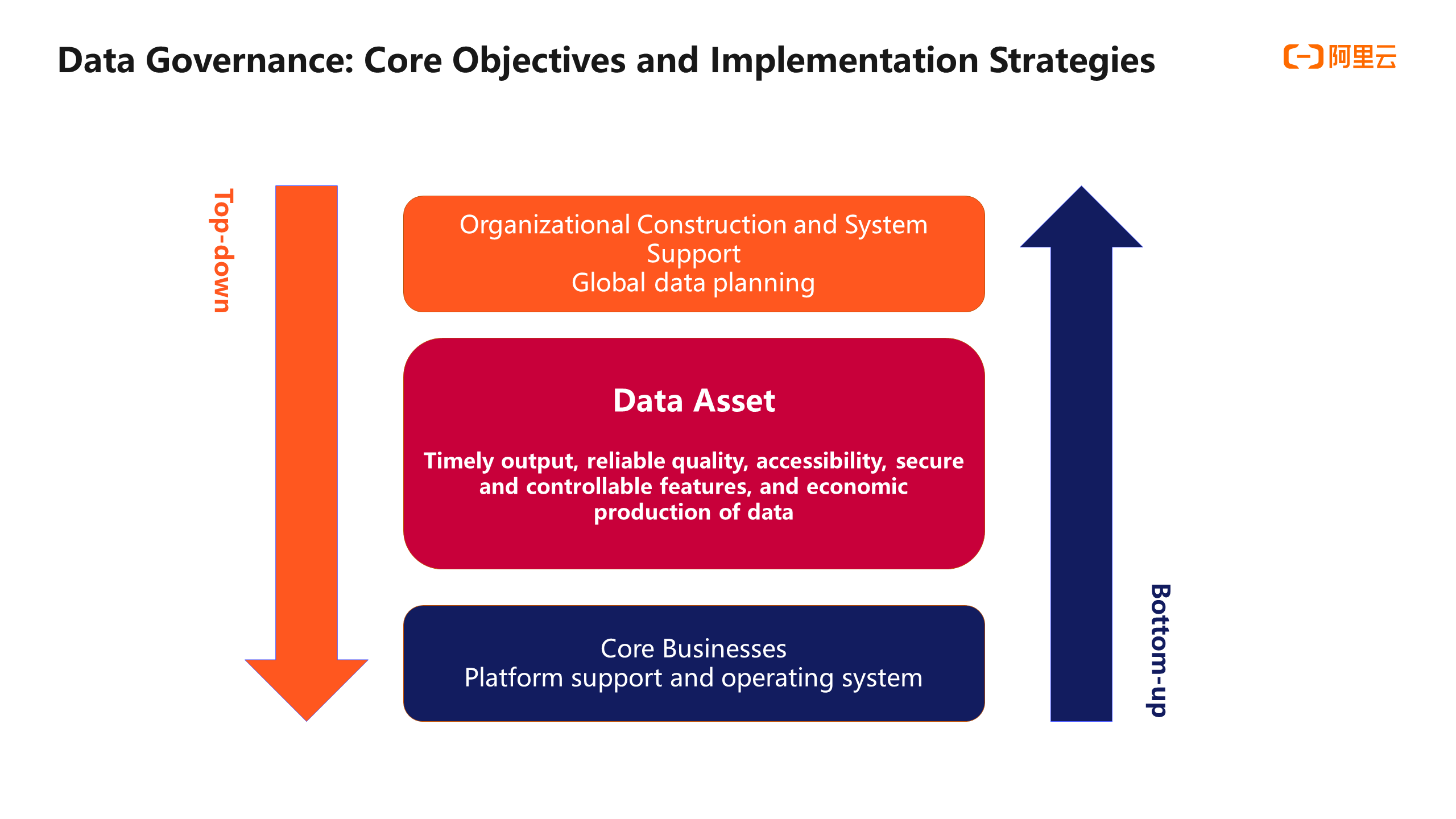
Data governance is driven by a close combination of the upper and lower levels, followed by the looping evolution. The demand pyramid of data governance also gives inspiration for data governance. We can plan the blueprint of data governance as a whole, but we need to implement it in stages. At different stages, the enterprise focuses on different demands of data governance. We recommend combining the situation of the enterprise, focusing on the key demands, and letting the functions gradually iterate.
There are two keywords: EB-level and tens of millions of tasks/day. The current situation is that the total data stored by Alibaba has reached the EB level, and the number of offline data tasks exceeds 10,000,000 per day. Moreover, they are increasing substantially, which means huge storage and computing costs. Therefore, the core demand of data governance in Alibaba at this stage has evolved to the top of the pyramid, which focuses on costs.
Alibaba can save one billion every year through data governance, which is a remarkable achievement. Within Alibaba, data governance can be effectively implemented with contributions from four aspects: organization construction, system guarantee, platform support, and operation.
Alibaba has established a data governance workgroup, which is affiliated with the Alibaba Digital Economy Data Professional Committee (a tier-1 organization). Members of the workgroup mainly include a data asset management team, which is independent of all BUs, the people responsible for data governance of each BU, and the people in charge of the data platforms. The core work of this workgroup includes formulating Alibaba Group specifications, determining governance goals, implementing governance, and maintaining the health of storage and computing. The data governance workgroup is given the right to directly influence the data production budget of each BU, which is an important power. The annual budget that a BU can get is closely related to how the BU accomplished the data governance goal of the previous year. Having a voice in the budget formulation is also a decisive factor for the data governance workgroup to implement governance.
In terms of system guarantee, Alibaba Group has formulated Group-wide specifications on data asset governance, which are mainly used to clarify the responsibilities and rights of each entity. At the same time, working rules for data governance are also formulated in detail, such as specifications for data model architecture and data R&D, principles of data quality assurance, and guidelines for data security management.
In terms of platforms, the data middle platform and offline data processing of Alibaba are built based on MaxCompute and DataWorks. MaxCompute is an engine for storing and computing EB-level data. It is fully developed and managed by Alibaba and provides storage and computing services for large amounts of data. DataWorks can be regarded as an operating system of MaxCompute. Based on the basic capabilities of MaxCompute, DataWorks provides all-around product services, such as data integration, data development, data map, data quality, data security, and data services. The close cooperation between the two platforms provides strong platform support for the implementation of data governance.
Three measures are taken in terms of operation. First, the resource consumption bill is sent to the resource user weekly, so the user can track the use of resources. Second, special governance activities are held regularly to implement optimization. Third, the best and worst governance list is published Group-wide to drive the implementation of data governance.
The key is to quantify the governance efforts with data. One of the core reference indicators in the best and worst list is the health score, which evaluates the health of storage and computing. If the health score is low, constraints are enabled until the person in charge completes related governance operations and raises the health score. When constraints are enabled, resource use is limited in the development environment, and tasks cannot be submitted or run.
The following figure shows the top ten technology trends in data and analytics in 2020 from Gartner, with two implications:
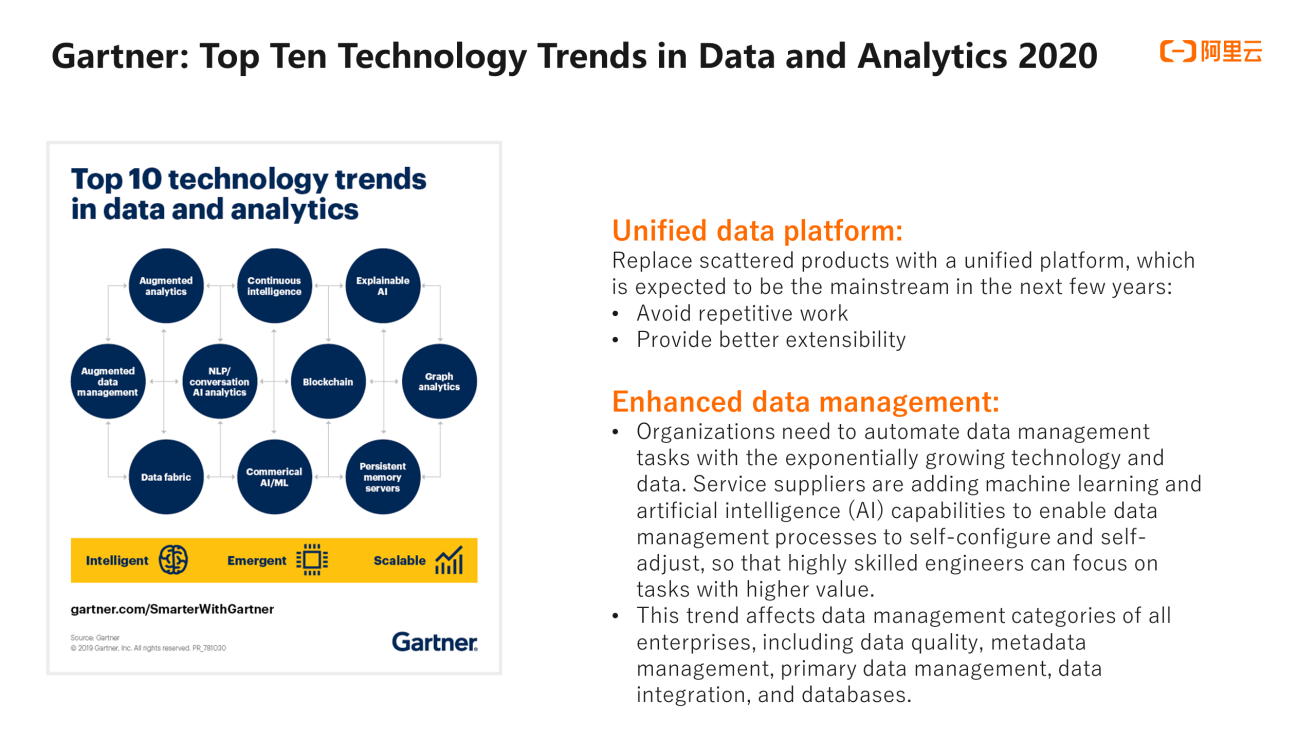
First, the introduction of technologies causes new trends and demands to emerge one after another. These trends are more or less related to each other. Therefore, it is necessary to build a unified data platform to avoid repetitive work and improve extensibility.
Second, we should develop enhanced data management services. The data platform needs to provide more powerful and convenient functions by introducing machine learning and AI to free the platform users for other important tasks.
The idea of DataWorks product design coincides with these two implications. In Data Governance, DataWorks introduces many algorithm technologies to assist users using the platform. Many people may wonder whether the core of data governance is personnel management. If you manage people well, data governance is implemented. However, the objects of governance are two objective entities to DataWorks, namely data and the task of producing data rather than people. DataWorks follows the idea of data governance based on data. It aims to serve platform users through the product capabilities of this platform and assist in the effective implementation of data governance. Based on this idea, DataWorks provides a series of product modules, such as task O&M, data security, data asset management, and resource optimization.
Next, we will introduce product modules corresponding to the demand levels of data governance.
The first-level demand of data governance is the timely output of data. We recommend using the intelligent monitoring function of the O&M Center to meet this demand. It is a baseline monitoring technology created by DataWorks and granted as the national patent. It is also one of the core functions that Alibaba widely uses to ensure the stability and timeliness of business data production, especially during the Double 11 Shopping Festival. DataWorks provides a wide range of maintenance operations for offline and real-time tasks in the O&M Center, such as batch re-execution of failed tasks, running of historical tasks with supplemented data, and intelligent diagnosis. These operations can save time for task O&M.
Another common cause of delay in task output is competition for resources. We recommend assigning these tasks to exclusive resource groups for tasks that require high timeliness. If task delay is caused by engine constraints, you can raise the upper limit of the quota of MaxCompute computing resources.
The Data Quality module provided by DataWorks can verify the correctness and completeness of data output. We introduced the functions in detail earlier in the introduction to the Data Quality module. There are two key points. First, DataWorks supports the configuration of dynamic threshold rules and automatic recommendation of rules, which is a featured function that introduces AI and algorithms. Second, quality monitoring and task scheduling are strongly associated. A strong alarm rule can be designed to block the scheduling of tasks if a quality problem occurs. Once a quality problem occurs, the scheduling is paused, and an alert is sent to the node owner to handle it in time. This prevents the spread of the quality problem.
DataWorks provides the Data Map module to make data available and reusable. The following figure shows the features of the Data Map module.
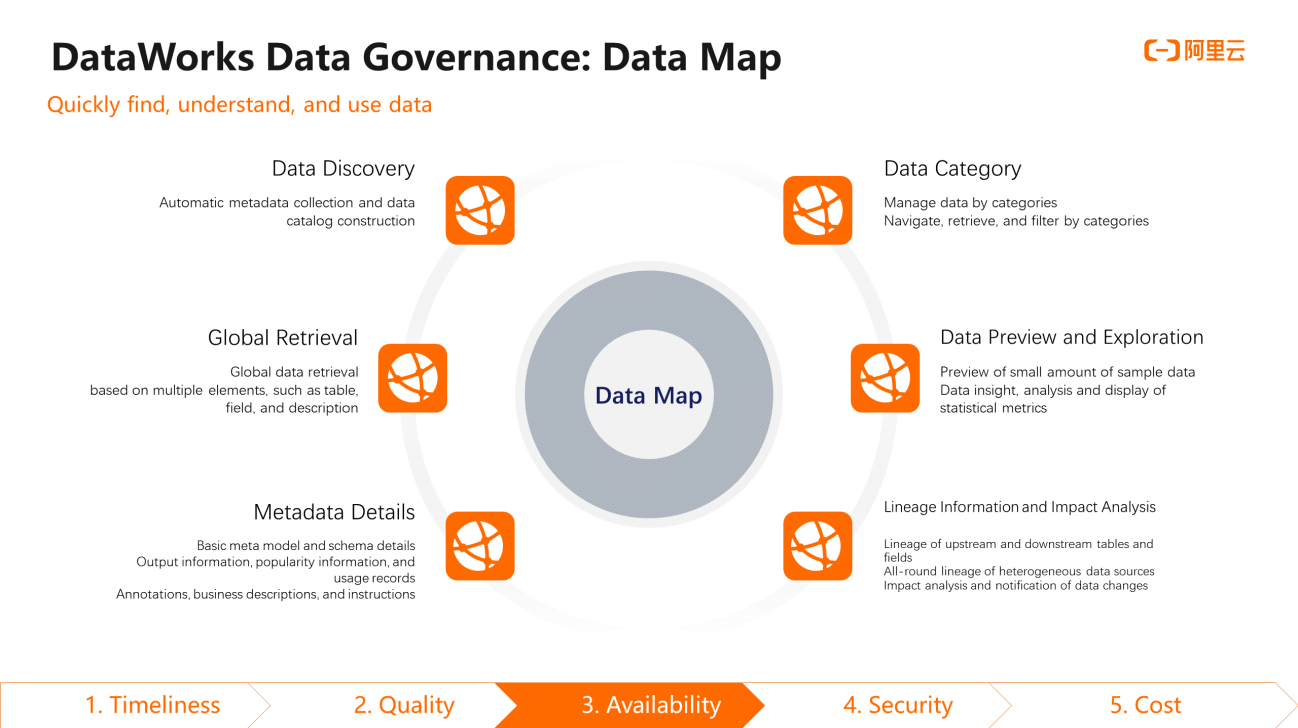
The ultimate goal of these data searching and understanding features is to improve the efficiency of data search and use so data can be fully reused. As a result, costs caused by data reproduction and storage can be reduced.
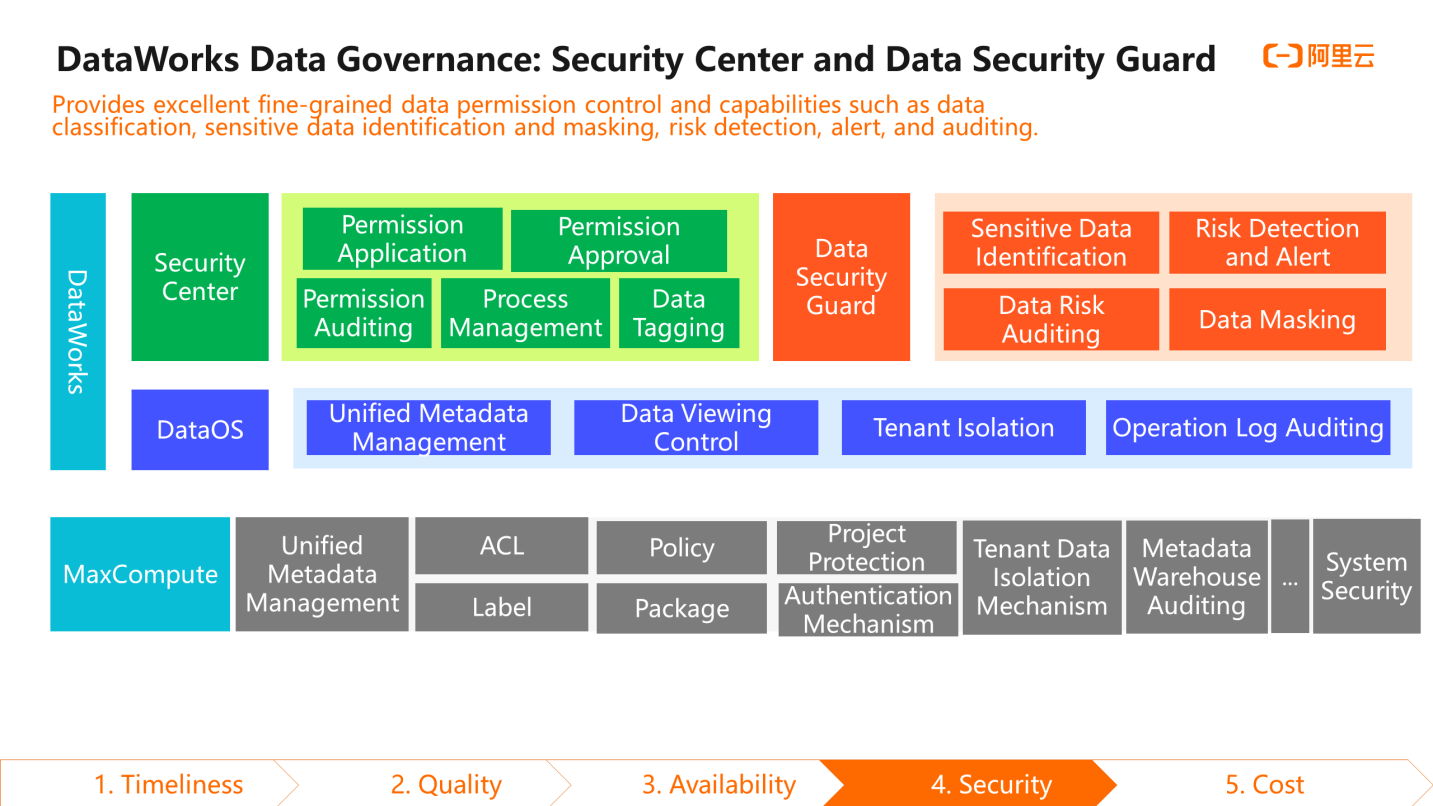
In terms of data security, DataWorks provides two functional modules: Security Center and Data Security Guard. The Security Center is used to process table permission applications, approvals, and audits. Data Security Guard provides financial-level identification and protection of sensitive data, including risk identification and warning, data risk auditing, and data masking. These functions are closely linked with other functional modules. For example, the user can configure data masking capabilities to protect sensitive data from leaking on the query results page of Data Development or the data preview page of Data Map.
When the scale of data volume or the number of data production tasks reaches a high level, the demand for cost control becomes stronger. Therefore, DataWorks provides Global Asset Inventory and Resource Optimization function modules, which enable users to perform asset inventory of the entire organization and view the total amount, trend, and distribution of data assets. Based on the idea of data governance, DataWorks provides specific optimization suggestions in three dimensions through intelligent analysis of the all-around metadata of the computing engine and platform: synchronous tasks, computing, and storage.
For example, a table has a long lifecycle but is not fully used, or the SQL is not well written, resulting in a brute-force scan. These situations bring a waste of resources. DataWorks analyzes the situations, generates governance items, and provides corresponding optimization suggestions to the owner.
The hero behind DataWorks data governance is the MaxCompute engine with extreme elasticity, flexibility, stability, and industry-leading architecture solutions. The technological innovation, evolution, and optimization in storage and computing offered by MaxCompute are the main reasons why Alibaba can save up to RMB 1,000,000,000 in costs annually. Technical improvements verified by the internal businesses of Alibaba are output to the public cloud. For example, the cost of data calculation and storage per unit decreases year by year. The resource consumption of a single SQL operation is also decreasing. Technological progress is saving costs for everyone.
MaxCompute has introduced a series of innovations in resource usage modes to help save costs, such as subscriptions, quota groups by time, and a mixed choice of pay-as-you-go + subscription.
Users that fully use MaxCompute should be impressed with its stability. Operation and maintenance are costly, especially when the services are needed at night. Processing tasks offline are mostly run at night, and users encounter problems due to the platform instability. Operation and maintenance are also labor-consuming and generate hidden costs. The MaxCompute engine has great advantages over open-source self-built solutions in terms of stability.
The combination of MaxCompute and DataWorks provides complete and rich product capabilities. It is also a solution that Alibaba has been using. It has been verified by real businesses for over ten years.
First of all, DataWorks has introduced the revised Comprehensive Data Governance. In the latest version, users can focus on and use the product functions needed from three different perspectives: data production, data usage, and data management. In the latest version, DataWorks provides a series of new product capabilities. The following figure is a summary:

In terms of metadata management, Data Map of DataWorks supports metadata collection from the 13 most commonly used data sources on the cloud, including MaxCompute, E-MapReduce, Hologres, ADB, and ApsaraDB RDS. Based on this, a large lineage map of heterogeneous data is built. In terms of data security, DataWorks provides the latest data traceability feature and blockchain-based data flow security products. In terms of maintenance and monitoring, the services are made mobile. Users can handle alerts from mobile phones, saving the time of maintenance at night. At the same time, alerts can be sent to the mobile phone.
DataWorks will also release capabilities, including stability governance, PDCA mechanism, and closed management loop. At the same time, the development team plans to export the health score mechanism, which is one of the best practices of Alibaba. In terms of openness, DataWorks recently provided a full set of open APIs, open data, and open messages to enable users to customize data governance based on the metadata information of DataWorks.
In terms of ecological cooperation, DataWorks cooperates with excellent partners in the industry to build and export joint solutions. Two examples of joint solutions are listed below:
The first is the management platform for data middle platform models, which is jointly provided by DataWorks and Datablau. The second is the integrated data governance solution provided by DataWorks and the DGOffice of DGWorkshop. It provides customers with full-site consulting services in the mode of consultation + products and carries out all-around governance, covering the full data lifecycle. Data governance is an industry-specific work. DGOffice has accumulated rich experience in data governance in many industries, so it is complementary to DataWorks.
If you need consultation, DataWorks and DGWorkshop can provide joint solutions and offer services from consultation to the implementation of the solution.
DataStudio: The Core Tool for Reducing Costs and Improving Efficiency

1,320 posts | 464 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - March 4, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Community - March 21, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Community - March 29, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Community - March 21, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Community - March 7, 2022
Alibaba EMR - July 9, 2021

1,320 posts | 464 followers
Follow Bastionhost
Bastionhost
A unified, efficient, and secure platform that provides cloud-based O&M, access control, and operation audit.
Learn More Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Alibaba Cloud provides big data consulting services to help enterprises leverage advanced data technology.
Learn More MaxCompute
MaxCompute
Conduct large-scale data warehousing with MaxCompute
Learn More Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Alibaba Cloud experts provide retailers with a lightweight and customized big data consulting service to help you assess your big data maturity and plan your big data journey.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Community