By Yunlei
Contributed by Alibaba Cloud Storage
Part 1 of this series discussed Presto's architecture. Presto is a memory computing engine, which means it must implement fine-grained memory management to ensure the orderly and smooth execution of queries, avoiding cases such as starvation and deadlocks.
Presto uses a logical memory pool to manage different types of memory requirements. Presto divides the entire memory into System Pool, Reserved Pool, and General Pool.
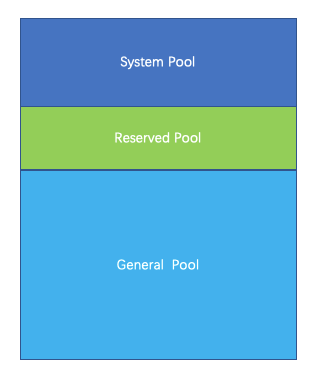
System Pool is used for the memory used by the system. For example, if data is passed between machines, the buffer is maintained in the memory. This part of the memory is mounted under the system name.
Why do we need to reserve memory? Why is the reserved memory equal to the maximum memory used by a query on the machine?
If there is no Reserved Pool, a query that consumes a lot of memory starts to run when the query is large and the memory space is almost occupied. However, there is no memory space for this query to run at this time, and this query has been mounted to wait for available memory. However, after other small memory queries finish running, new small memory queries are added. Small memory queries take up a small amount of memory, so it is easy to find available memory. As such, the large memory query hangs until it starves to death.
If you want to prevent the situation, a space must be reserved for the large memory query to run. The size of the reserved space is equal to the maximum memory that the query allows. Presto selects a query with the largest memory usage every second and allows it to use the reserved pool to avoid the situation where no available memory is there for the query to run.
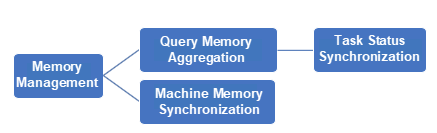
Presto memory management is divided into two parts:
1. Query Memory Management
2. Machine Memory Management
After the query and machine memory are aggregated, the coordinator selects the query with the largest memory usage and assigns it to the Reserved Pool.
Memory management is managed by the coordinator, which determines every second to specify that a query can use reserved memory on all machines. However, here is the problem. If the query is not run on a machine, is it a waste of memory reserved by the machine? Why not pick out the largest task execution on a single machine? The reason is deadlock. If the query has reserved memory on other machines, the execution will end soon. However, the task is not the largest on a machine and cannot be run all the time. As a result, the query fails to be ended.
Disclaimer: The views expressed herein are for reference only and don't necessarily represent the official views of Alibaba Cloud.
An In-Depth Understanding of Presto (1): Presto Architecture

1,320 posts | 464 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - February 8, 2023
降云 - January 12, 2021
Alibaba Cloud Community - February 10, 2023
Apache Flink Community China - September 27, 2020
Alibaba EMR - April 2, 2021
vboylin - May 10, 2019

1,320 posts | 464 followers
Follow Storage Capacity Unit
Storage Capacity Unit
Plan and optimize your storage budget with flexible storage services
Learn More Hybrid Cloud Storage
Hybrid Cloud Storage
A cost-effective, efficient and easy-to-manage hybrid cloud storage solution.
Learn More Hybrid Cloud Distributed Storage
Hybrid Cloud Distributed Storage
Provides scalable, distributed, and high-performance block storage and object storage services in a software-defined manner.
Learn More Data Lake Storage Solution
Data Lake Storage Solution
Build a Data Lake with Alibaba Cloud Object Storage Service (OSS) with 99.9999999999% (12 9s) availability, 99.995% SLA, and high scalability
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Community