By Zeng Qingguo (Yueda)
KubeVela 1.5 was released recently. This release brings more convenient application delivery capabilities to the community, including system observability, CloudShell terminals that move the Vela CLI to the browser, enhanced canary releases, and optimized multi-environment application delivery workflows. It also improved KubeVela's high extensibility as an application delivery platform. The community has started to promote the project to the CNCF Incubation stage. It has absorbed the practice sharing of multiple benchmark users in many community meetings, which proves the community's healthy development. The project is now mature to some extent, and its adoption has made periodical achievements, thanks to the contributions of more than 200 developers in the community.
KubeVela has released five major versions over the past year. Each iteration is a leap forward. The release of version 1.1 brought the ability to connect multiple clusters. Version 1.2/1.3 brought an extended system and a more developer-friendly experience. Version 1.4 introduced a security mechanism in the complete process. The release of 1.5 today brings us closer to KubeVela's vision of making application delivery and management easier. Along the way, we have stayed true to the same design philosophy and built a platform that automates the complexity of the underlying differentiated infrastructure without losing scalability. It helps application developers upgrade from business development to cloud-native R&D at a low cost. Technically, it focuses on the complete process from code to cloud and from application delivery to management. It refines the framework capabilities of connecting infrastructure based on the Open Application Model (OAM). As shown in Figure 1, KubeVela has covered the complete capabilities of application definition, delivery, O&M, and management, all of which are based on OAM scalability (OAM Definition) to connect to ecological projects in an addon way. In essence, each definition converts the experience of a specific capability into a reusable best practice module, which can be shared by enterprises or communities through addon packaging.
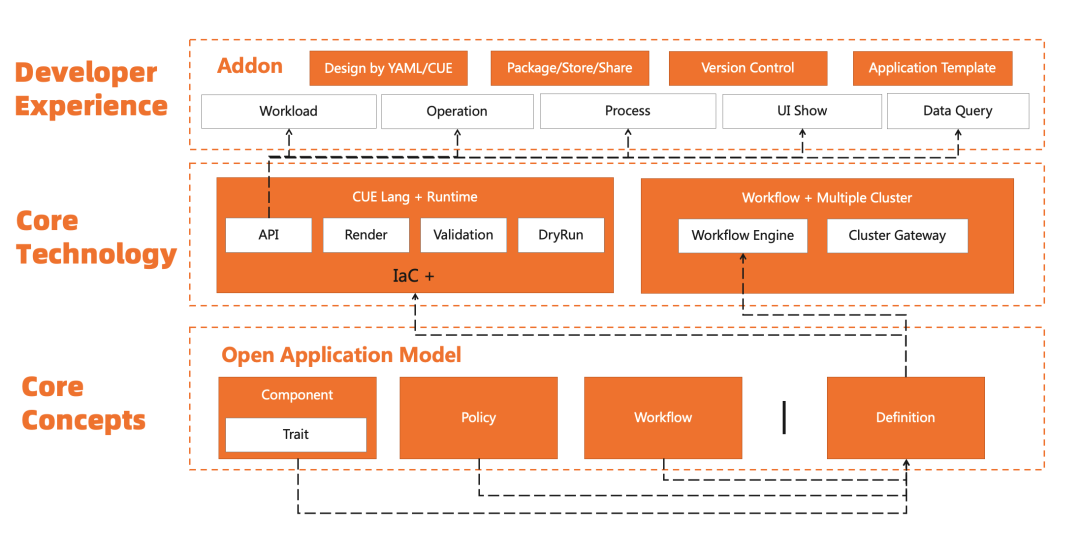
Figure 1: Core Structure of KubeVela Extensibility
The blossoming of atomic capabilities in cloud-native is an asset that raises the threshold in the field. Platform builders need to learn a large number of open-source projects and aggregate experience in multiple fields. It often takes months or longer to build a cloud-native support platform for the enterprise. However, the platform often passes the complexity to the application developer, which means they have to learn a lot of additional knowledge. KubeVela's design concept and existing technical achievements may help you quickly enter the cloud-native world. KubeVela's major addon integration specifications and unified application delivery experience in version 1.5 and previous versions have solved the problem of discrete atomic capabilities in the cloud-native field.
The KubeVela addon mechanism has been popular among community users since version 1.2. There are nearly 50 addons in the community addon repository. Nearly 50 developers participated in the contribution of the addon.
Please see this link for more information
Starting from version 1.5, addon developers could have a better experience. Addon definition, distribution, and visual management are all improved. In addition to using YAML to define addons, developers can fully use CUE to define addons if they want a more flexible combination of addon resources and higher-level parametric control. The current specifications for addon definitions include the following parts:
Please refer to the document for details.
Here is an example of integrating the delivery capability of the Helm Chart package. Currently, projects in the community like FluxCD or ArgoCD provide the atomic capability of deploying Chart packages. Their implementations are different, and each has its advantages. For KubeVela users, these two projects can be introduced through addons. As shown in Figure 2, we need to define a standard API for the end user to expose the necessary parameters to the end user according to the specific situation of the enterprise.
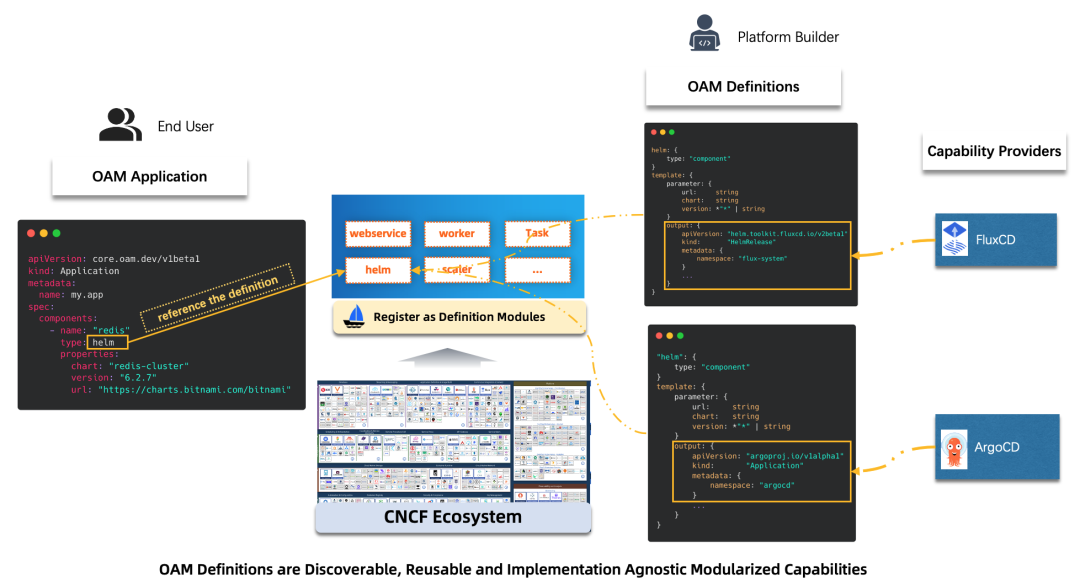
Figure 2: Process of KubeVela Extending the Helm Chart Package
As shown in Figure 3, according to the standard API, the frontend UI can automatically generate the corresponding interactive page to help the end user easily and conveniently deploy the Helm Chart package. The platform side automatically generates the driver configuration of the underlying capability based on the user's input parameters and addon definitions and intelligently sends the relevant status feedback to the user. These are based on addon specifications, such as integrating FluxCD. This project includes multiple controllers providing different atomic capabilities. First, we use template.cue to define the deployment method of FluxCD and deploy different components based on different parameter inputs. Then, the user experience is defined by definitions and schema directories.
Please see this link for more information.
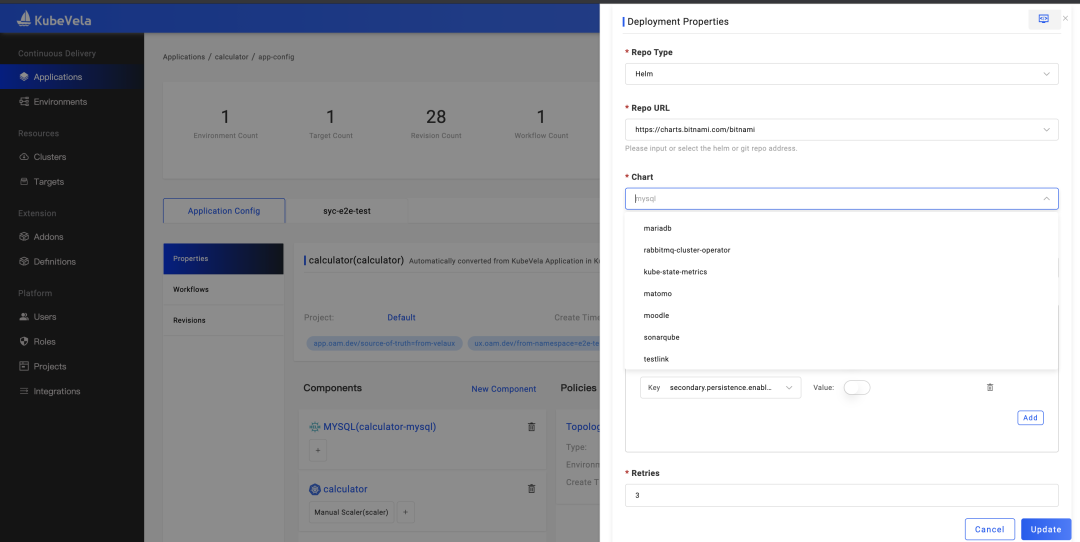
Figure 3: Interaction for KubeVela to Deliver Helm Chart Packages
The system of application observability is closely related to application release. A good application observability system can make the management of application reliability easy. The KubeVela community includes application observability into the core features. In version 1.5, the community selected the KubeVela system observability as a case for system capability development. The following key points have been realized:
Figure 4 shows the dashboard of KubeVela system operating indicators. The dashboard is automatically generated through the IaC system. You only need to enable the corresponding addon.
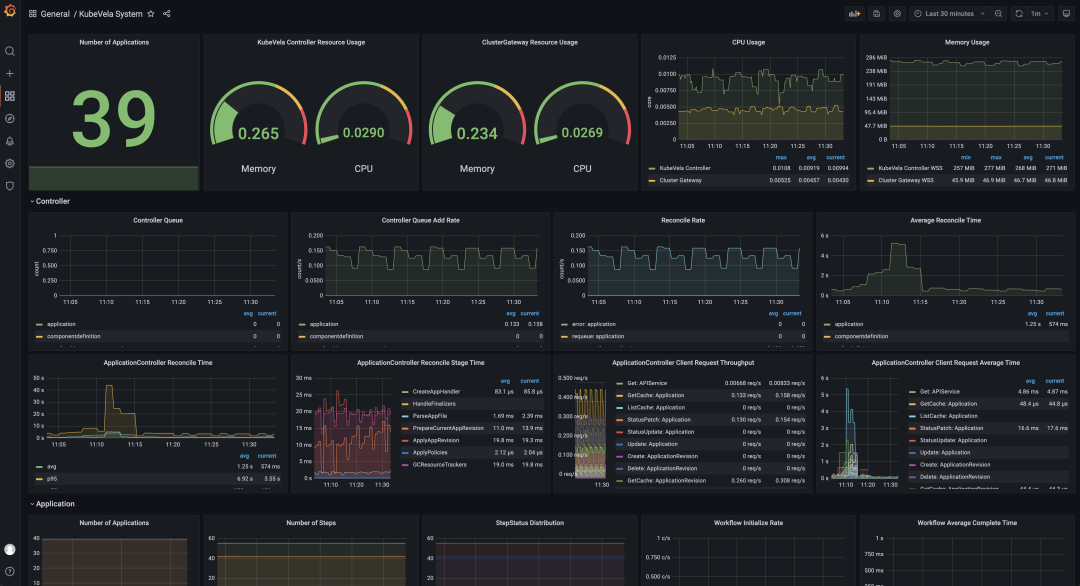
Figure 4: KubeVela System Observable Dashboard
Figure 5 shows the monitoring dashboard of the Kubernetes API Server service connected to KubeVela. Use addons to issue Exporters to all sub-clusters, expose data to the Prometheus service of each cluster, and aggregate it to the control cluster for centralized visualization. You can complete the data monitoring and dashboard access of many clusters at the same time.
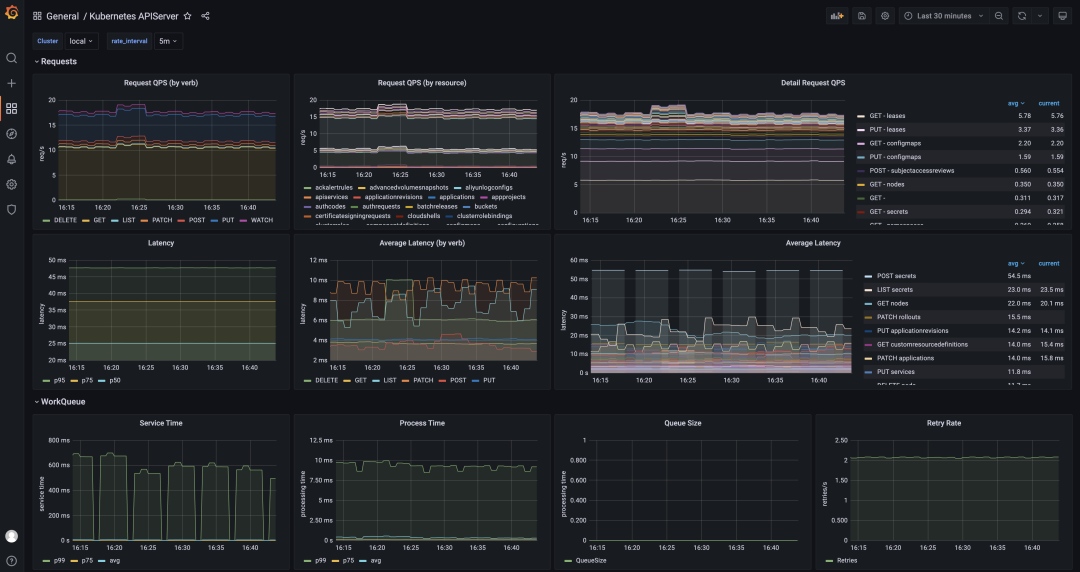
Figure 5: KubeVela Multi-Cluster API Observation Dashboard
In the next release, the community will gradually integrate the unified description and delivery of application observability into the application delivery process. It covers Metric, Logger, and Tracing data acquisition, intermediate processing and transmission, storage and analysis, alerts and visualizations, and applications to the complete process of the application release workflow.
Reference: http://kubevela.net/docs/platform-engineers/operations/observability
Manipulating application delivery through a CLI black screen is convenient, easily replicated, and can be done in batches. Developers are fond of it. Delivering application interactions through UI is more elegant. Process operations help reduce learning costs and achieve stricter enterprise security controls. A high degree of visualization can help us master the application and perform relevant operations anytime and anywhere. KubeVela was very different in the CLI and UI dimensions in the past version, and data in the two dimensions do not communicate with each other. If the two terminal methods can be combined, application delivery and management can be smoother. In version 1.5, KubeVela introduced the CloudShell addon, which provides a Web Shell terminal for UI users. The unified portal solves the problem of CLI and UI separation and brings more capabilities. The main changes to this process are listed below:
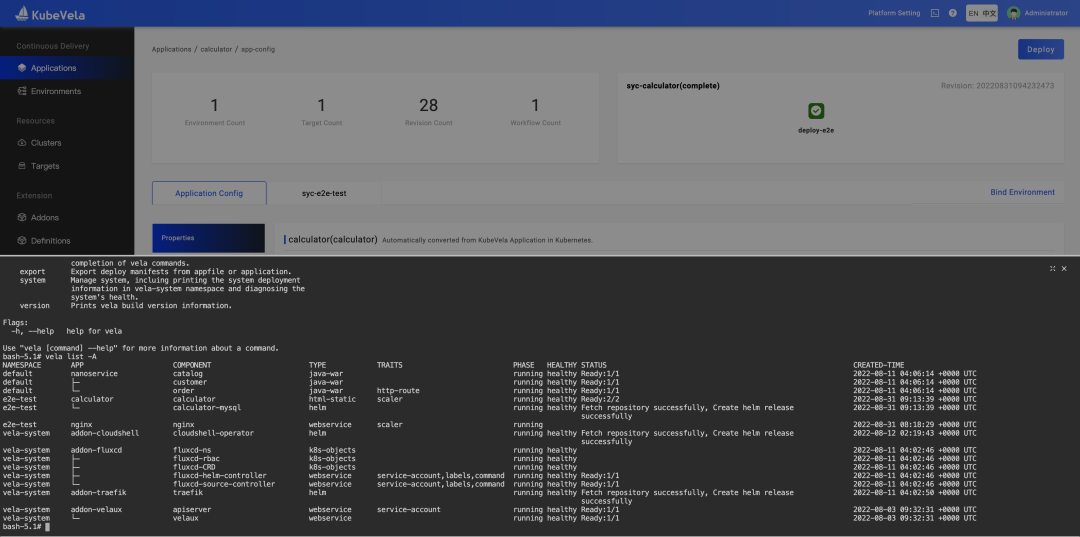
Figure 6: KubeVela CloudShell Operating Terminal
The KubeVela community incubated the Rollout project in the early days, similar to the implementation model of Argo Rollout. It works in the form of a new workload, mainly realizing the ability to release in batches. With the development of the community, KubeVela focuses more on the application global control layer and addon extension capabilities. Therefore, the rollout implementation at the workload level has been transferred to the OpenKruise community. With the joint efforts of both parties, canary release capabilities can be implemented for various workloads (such as native Deployment, StatefulSet, and OpenKruise extended workload CloneSet). At the same time, when it coexists with the Helm delivery mode in KubeVela, it can implement the canary release for Helm chart package applications without any changes. This is innovative in the industry and very convenient for users. Kruise Rollout is integrated into the KubeVela ecosystem as an addon. KubeVela users only need to enable addons to configure Rollout Trait in application components. At the same time, it can cooperate with gateway rules (such as Gateway and HTTPRoute). This implementation has the following advantages:
Reference: http://kubevela.net/docs/end-user/traits/rollout
VelaUX has had the multi-environment deployment capability since its launch. Until version 1.5, it supports the differentiation of multiple environments for user visual editing, truly matching the needs of user multi-environment application release. Override Policy configurations support the dimension differentiation of environments, clusters, or namespaces and the unified management of application baseline and configurations..
As shown in Figure 7, the Application Policy has a variety of available options built in, including differentiated configuration, application multi-cluster policies, application maintenance policies, and GC policies. Users can easily configure corresponding policies according to their needs through UI guidance.
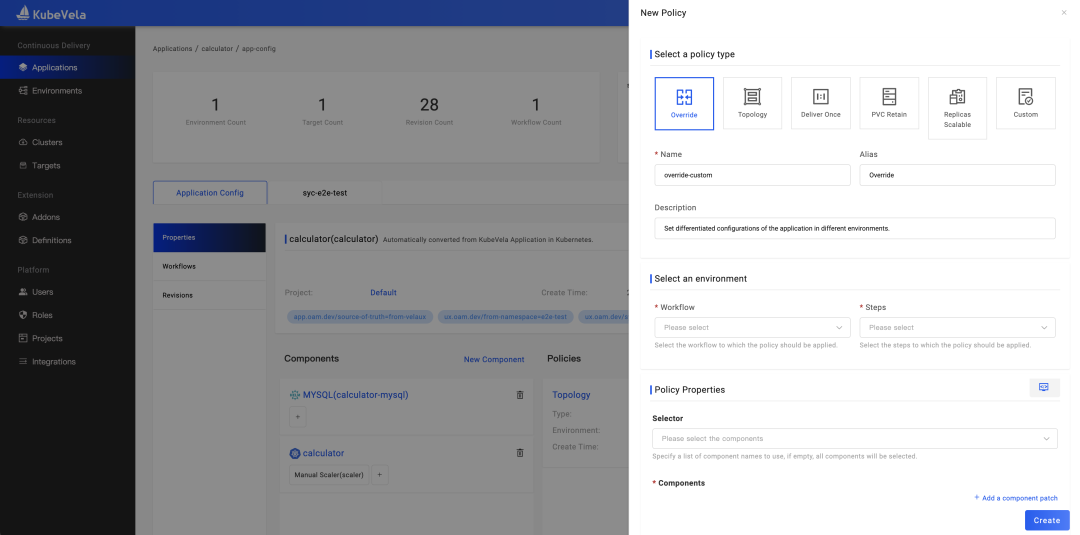
Figure 7: KubeVela Policy Add/Edit Window
In version 1.5, the following convenient features are added before and after deployment for different environments:
Reference: http://kubevela.net/docs/tutorials/multi-env
In addition to the preceding addon capabilities, a large number of updates have been made to the application engine. The performance is significantly improved, and the CPU consumption during workflow execution is reduced by 75%. The number of parallel executions has increased significantly. The important changes are listed below:
Please refer to this link for more information about changes.
Overall, KubeVela 1.5 has made significant progress in multiple dimensions (such as product capabilities, community ecology, and benchmark users). User cases include finance, intelligent manufacturing, the Internet, and other industries. We expect more users to share practical experiences and help the KubeVela community find a more accurate way forward. Version 1.6 plans to bring more complete application observability, independent application workflow capabilities, continuous release control of multiple applications, and collaboration with observable systems. Developers with relevant needs and ideas can participate in community discussions at any time.
You can learn more about KubeVela and the OAM project through the following materials:
github.com/oam-dev/kubevela
Welcome to Star/Watch/Fork!
(Chinese and English documents have been provided since Version 1.1. We welcome developers to translate more language documents.)
Kruise Rollout: Flexible and Pluggable Progressive Rollout Framework

503 posts | 48 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - September 16, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - March 20, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - January 16, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - March 1, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - January 9, 2023
Aliware - March 22, 2021

503 posts | 48 followers
Follow Function Compute
Function Compute
Alibaba Cloud Function Compute is a fully-managed event-driven compute service. It allows you to focus on writing and uploading code without the need to manage infrastructure such as servers.
Learn More Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Accelerate and secure the development, deployment, and management of containerized applications cost-effectively.
Learn More Lindorm
Lindorm
Lindorm is an elastic cloud-native database service that supports multiple data models. It is capable of processing various types of data and is compatible with multiple database engine, such as Apache HBase®, Apache Cassandra®, and OpenTSDB.
Learn More PolarDB for MySQL
PolarDB for MySQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for MySQL is a cloud-native relational database service 100% compatible with MySQL.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native Community